Current Standards for Industrial Factory Overhead Cranes
January 22, 2026 07:18 AM
In the field of industrial production, the factory overhead crane is equipment that plays an extremely important role in lifting, lowering, and moving heavy goods and equipment. However, to ensure effective and safe operation, the crane system needs to meet certain technical standards and legal regulations. 1. What is a Factory Overhead Crane? A factory […]
In the field of industrial production, the factory overhead crane is equipment that plays an extremely important role in lifting, lowering, and moving heavy goods and equipment. However, to ensure effective and safe operation, the crane system needs to meet certain technical standards and legal regulations.
1. What is a Factory Overhead Crane?
A factory overhead crane (also known as a bridge crane) is specialized lifting equipment installed permanently in the factory to move goods and heavy objects horizontally and vertically within a limited range. This equipment is commonly used in industries such as mechanics, machine manufacturing, logistics, metallurgy, steel production, etc.
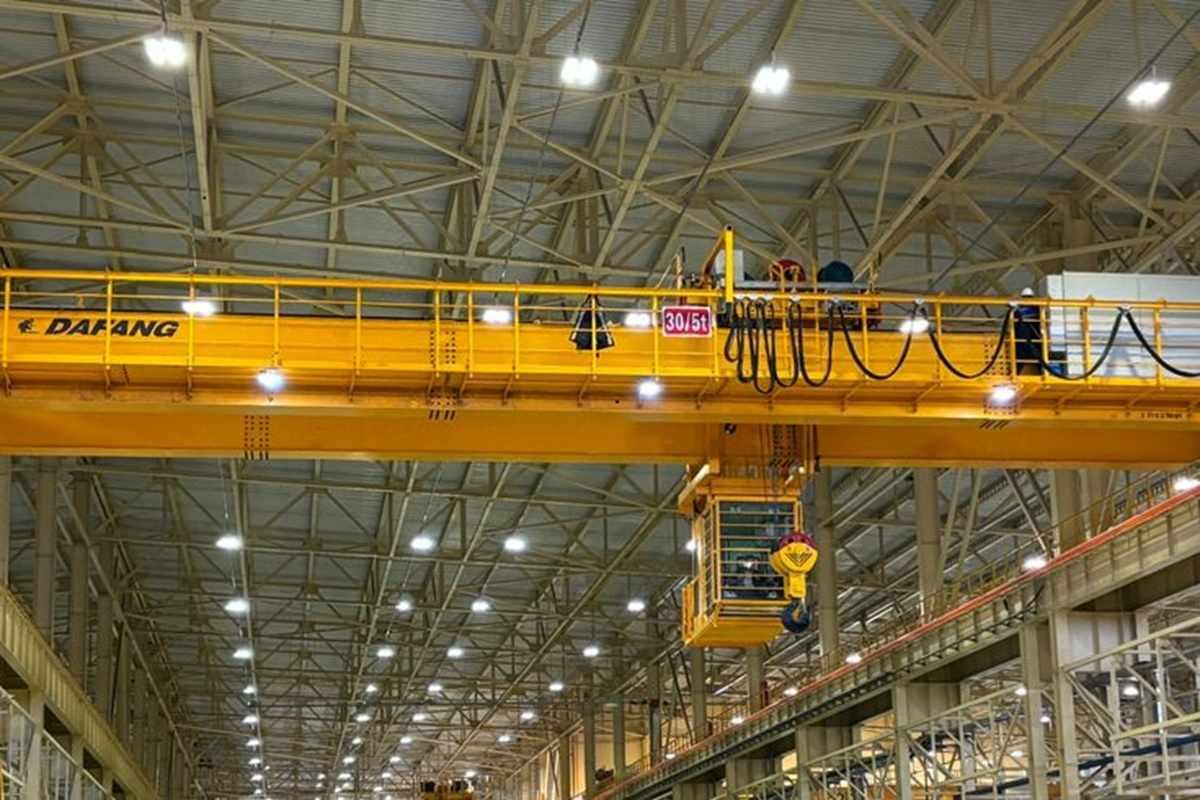

Overhead crane system installed in the factory.
The crane usually consists of main components including: main girder, end carriage (end truck), hoist (lifting device), rail system, drive motor, wheels, and electric control panel. Cranes have diverse lifting capacities, which can reach up to 500 tons, depending on the design and load requirements.
2. Common Types of Overhead Cranes Today
Depending on the structure, installation location, and purpose of use, factory overhead cranes are divided into many different types.
Single Girder Overhead Crane
This is a type of crane with only one main girder, usually used for light to medium loads (from 500kg to 10 tons). The advantage of a single girder crane is its simple design, light weight, low investment cost, and ease of maintenance. It is suitable for factories with limited space or not requiring large loads.
Double Girder Overhead Crane
The double girder crane has two parallel main girders, helping to increase rigidity and high load-bearing capacity (can be up to 50 tons or more). It is often used in heavy industries where lifting large equipment and continuous operation are required. Although the cost is higher, the performance and safety are also superior.
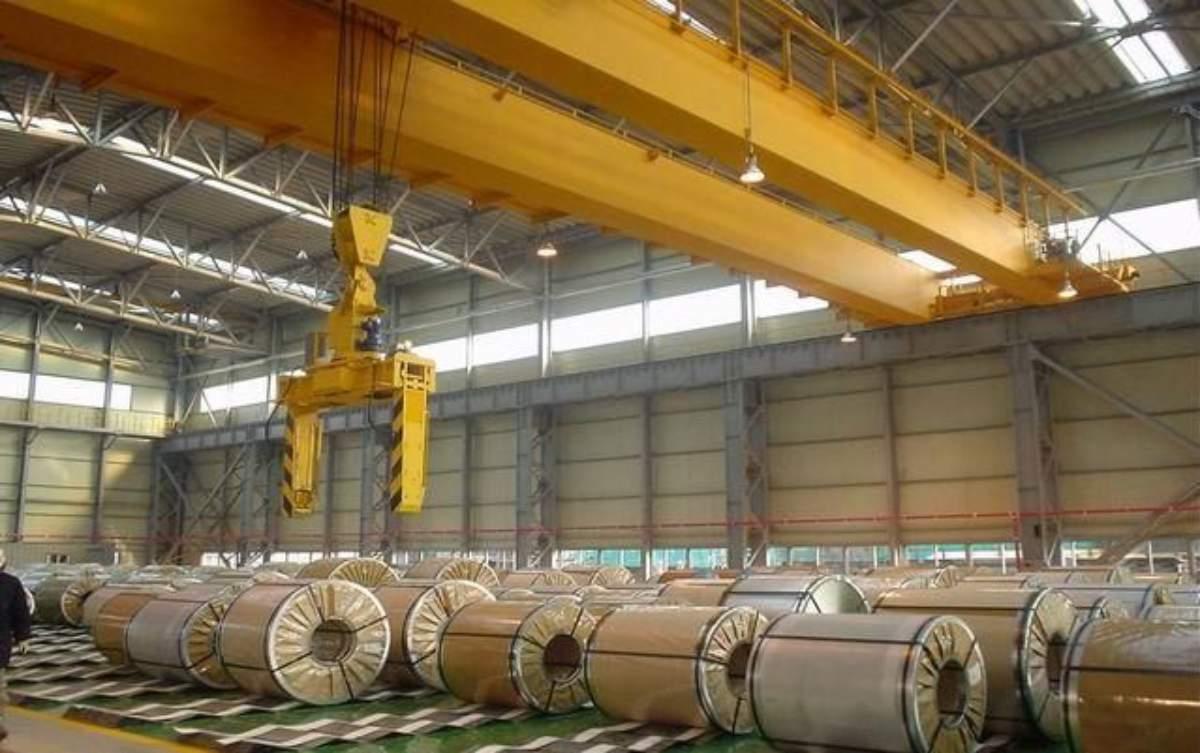

Double girder overhead crane.
Suspension Crane (Underhung Crane)
This is a type of crane with the main girder suspended below the factory roof beam system, instead of running on rails placed on columns like conventional cranes. Thanks to this installation feature, the suspension crane helps optimize space height, very suitable for factories with height limitations. However, this type of crane is usually only suitable for small to medium loads.
Semi-Gantry Crane
This type of crane has one end moving on a rail mounted on a column or wall, while the other end is firmly fixed to the factory wall structure (or moves on a ground rail). The semi-gantry crane is an economical and flexible choice, especially suitable for factories with asymmetrical structures or only needing lifting in a certain area without installing rails on both sides.
In addition to the common types above, there are specific crane lines such as:
- Jib Crane: Used to lift objects within a certain turning radius.
- Container Crane: Specialized for use in seaports, loading and unloading containers.
- Specialized Crane: Custom designed according to the specific requirements of each manufacturing industry.
3. Benefits of Installing Standard Cranes in Factories
A well-invested and technically operated crane system will create many advantages for the factory, from increasing processing speed to reducing risks during production.
3.1. Increasing Productivity and Operational Efficiency
When equipped with an overhead crane, the factory can perform heavy object moving operations quickly, accurately, and continuously. This is why cranes can help shorten the processing time of each stage, from loading raw materials to moving finished products out of the line. Beyond speed benefits, cranes also help maintain operational stability. With automatic control systems and smooth movement mechanisms, operations are uninterrupted, minimizing waiting time in the production process.
3.2. Ensuring Occupational Safety
Occupational accidents in factories often stem from manual operations with heavy objects when the workload requires continuous lifting and lowering of large equipment. For such situations, using human strength is no longer a safe or sustainable option. The overhead crane emerged as an alternative solution contributing to eliminating most injury risks from manual lifting and pulling. Modern crane models today are also integrated with many safety mechanisms such as load sensors, limit switches, or emergency stop functions, supporting the minimization of incidents during operation.
3.3. Saving Labor Costs and Production Time
Once supported by a crane, businesses do not need to mobilize too much manpower for heavy tasks such as lifting, pulling, and transporting materials. Stages that originally required a large number of workers to perform now only need one remote control technician. Moreover, the fast and accurate operation capability of the crane helps shorten the completion time of each order. When the production schedule is shortened, businesses can have more room to increase output, expand customers, or improve the ability to meet urgent orders, building a great advantage in a highly competitive environment.
3.4. Improving the Ability to Operate Heavy Industrial Equipment
In many manufacturing industries, especially mechanical engineering, the process of installing or moving large equipment such as machine molds, engines, steel frames… is a mandatory task. Not every type of lifting machine can meet the above requirements. Thanks to the high load-bearing design and flexible movement capability in three-dimensional space, the crane can perform these operations easily and accurately to the millimeter.
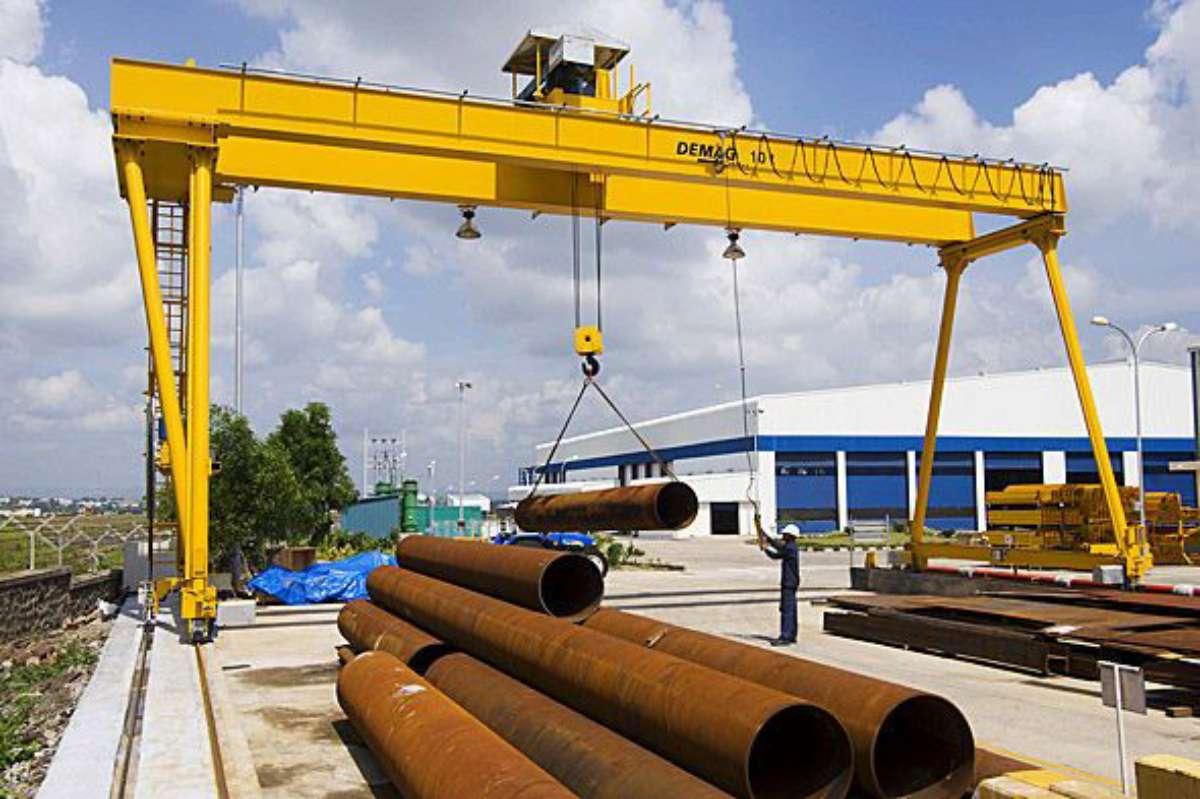

Application of cranes in moving large-sized items.
Most importantly, using a crane also helps protect industrial equipment itself from unwanted collisions or damage during installation. For high-value machinery requiring absolute precision, the stable control and positioning capability of the crane becomes an irreplaceable factor.
4. Current Technical Standards for Factory Overhead Cranes
To ensure safety and operational efficiency, factory overhead cranes need to comply with technical standards prescribed by Vietnam and international bodies. These standards will include guidelines for design, manufacturing, as well as regulations on inspection, use, and maintenance of equipment.
4.1. Structural Design Standards (TCVN 4244:2005, ISO 4301…)
- TCVN 4244:2005 regulates the design, manufacture, and technical inspection of lifting equipment, including requirements for materials, load-bearing structures, welds, and technical documents.
- ISO 4301-1:2016 classifies lifting equipment into classes M1–M8 based on load and operating cycle — helping to choose a configuration suitable for each purpose of use.
4.2. Load and Load-bearing Safety Standards
In the use of factory overhead cranes, it is necessary to apply ISO 8686-1 and FEM 1.001 to calculate static and dynamic loads and determine safety factors. The equipment must pass load tests to ensure no deformation or damage during use.
4.3. Electrical and Control System Standards
Cranes need to comply with IEC 60204-32 and TCVN 7447, ensuring a safe electrical system with protective devices such as:
- Emergency stop button.
- Limit switches.
- Water-resistant, dust-resistant control box (IP rating).
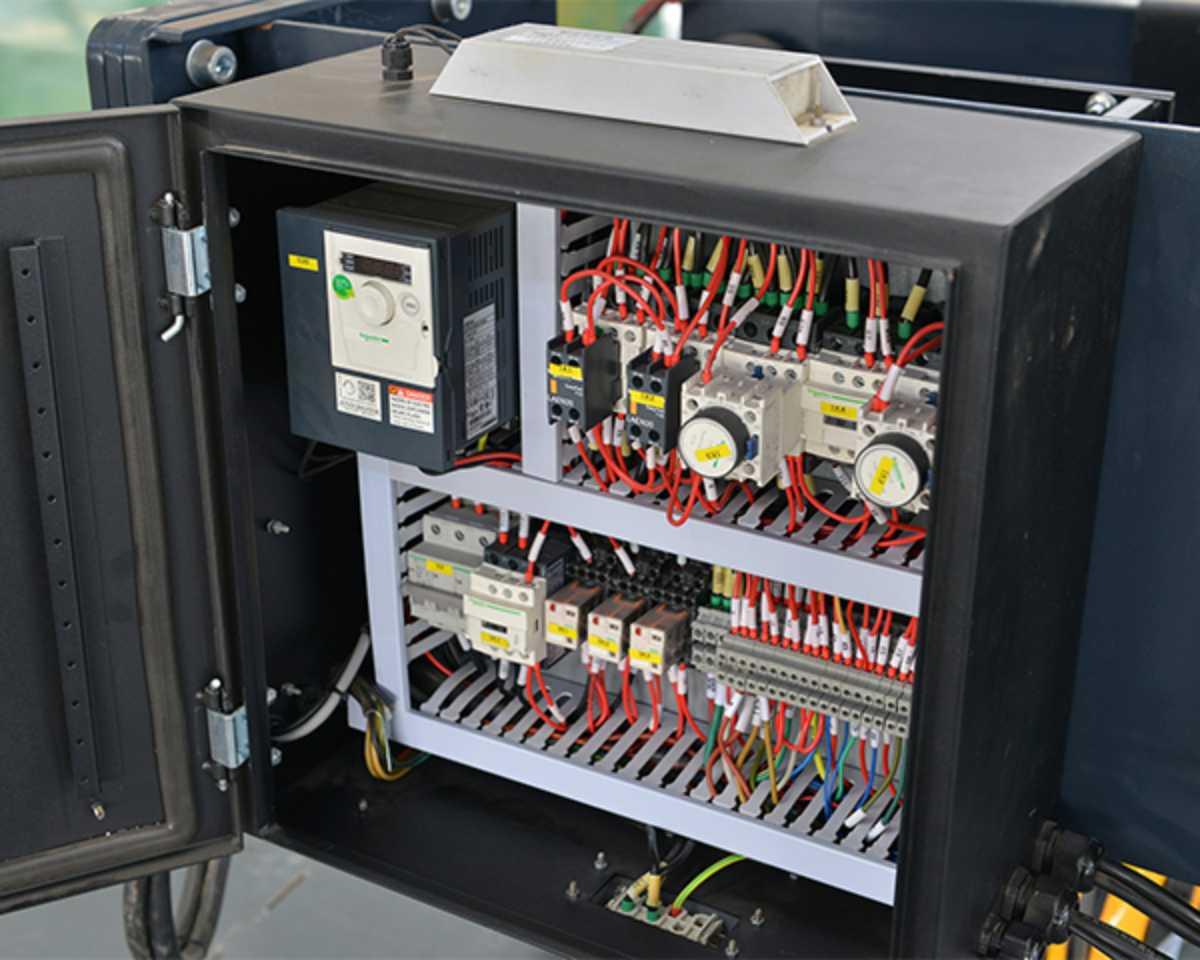

Crane control box.
4.4. Rail, Wheel, and Drive System Standards
TCVN 8630:2010 requires rails and wheels to have high straightness, be firmly attached, and have good wear resistance. The drive system needs brakes, sealed gearboxes, and shock absorbers for smooth, accurate operation.
4.5. Requirements for Operating Limits and Periodic Load Testing
During the design and operation of the crane, determining and setting operating limits such as maximum lifting load, travel length, and movement speed is mandatory. These limits are usually integrated into the control system through devices such as overload sensors, limit switches, and travel controllers, with the aim of ensuring the equipment does not exceed the allowed safety threshold. In addition, the crane needs to be load-tested periodically, especially after incidents or major repairs. Load tests, including static load tests and dynamic load tests, need to be conducted to assess the actual load-bearing capacity of the equipment, helping to detect potential damage in the structure and drive system early.
5. Legal Regulations and Safety Inspection of Cranes
Overhead cranes are special lifting equipment, falling under the list of strict technical safety inspection requirements. Therefore, besides complying with technical standards, businesses also need to fully perform legal procedures and periodic inspections according to current regulations.
5.1. Regulations of the Ministry of Labor – Invalids and Social Affairs (MOLISA)
According to Circular 07/2020/TT-BLĐTBXH issued on November 20, 2020, all lifting equipment such as overhead cranes, gantry cranes, hoists, etc., must undergo technical safety inspection in the following cases:
- Before being put into use for the first time.
- After repair or renovation affecting the load-bearing structure.
- When there are abnormal signs during operation.
- Periodically annually or according to manufacturer instructions.
This circular also clearly stipulates: only licensed inspection organizations are allowed to perform inspections and issue valid certificates.
5.2. Steps for Technical Safety Inspection of Cranes
According to Circular 07/2020/TT-BLĐTBXH and standard TCVN 4755:2008, the crane inspection process includes 4 main steps:
- Step 1: Check and receive the technical dossier of the equipment, including design drawings, material certificates, operation, and maintenance logs.
- Step 2: Check the actual site to assess the condition of the structure, mechanical system, electrical system, and safety devices.
- Step 3: Load testing, including static load test with load level ≥125% of nominal load and dynamic load test with 100% of nominal load, to check the stable operation capability of the crane.
- Step 4: Prepare inspection minutes and issue a valid certificate if the equipment meets requirements. If not, the crane must be repaired and re-inspected before use.
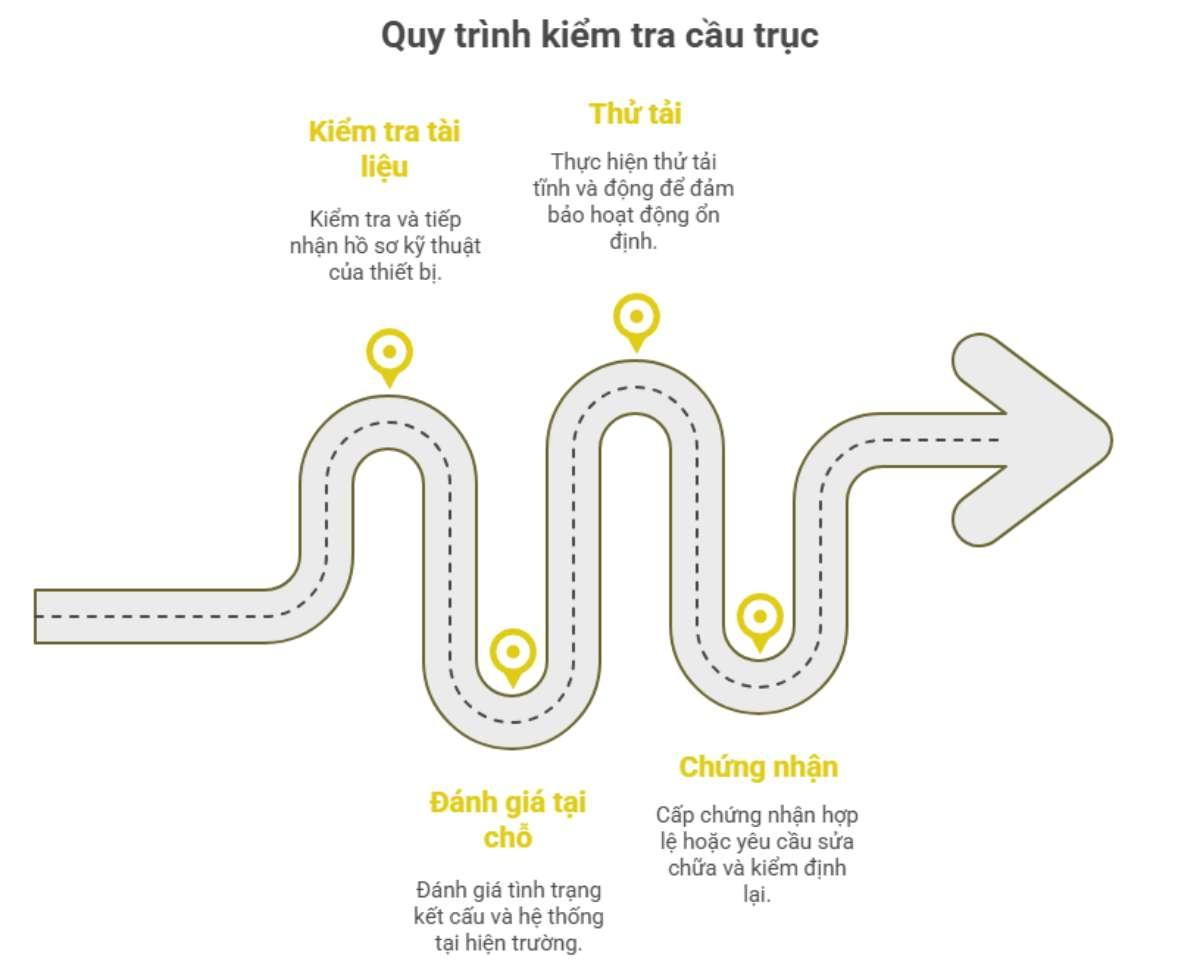
Steps for technical safety inspection of cranes.
5.3. Inspection Frequency and Mandatory Documents
The frequency of crane inspection is specified in Appendix I of Circular 07/2020/TT-BLĐTBXH. Specifically, the crane needs to be inspected for the first time before use, periodically every 12 months under normal conditions, and every 6 months if operating in harsh environments or with high frequency. In addition, irregular inspection is required after major repairs, structural changes, or serious incidents. Regarding inspection documents, businesses need to fully prepare documents such as equipment history (logbook), technical drawings, material certificates, maintenance and operation logs, previous inspection minutes (if any), and the latest load test results.
6. Factors to Consider When Choosing Cranes for Factories
6.1. Purpose of Use and Required Load
Not all cranes serve the same purpose. A heavy mechanical factory needs lifting equipment with large load capacity, operating continuously with high intensity. Meanwhile, logistics warehouses only need light cranes, flexible movement, and fast manipulation. Clearly identifying usage needs will help businesses choose the right type of crane and suitable technical specifications. This is a way to optimize investment costs while ensuring the equipment is not overloaded or over-capacity during operation.
6.2. Factory Area and Structure
Installation space is one of the most important technical factors. For factories with limited height or divided space, choosing a standard double girder crane will not be feasible. At this time, options such as suspension cranes or semi-gantry cranes can solve the space problem. On the other hand, the load-bearing capacity of the roof or wall structure also needs to be considered. Installing a crane unsuitable for the structure will lead to additional reinforcement costs or face safety risks during operation.
6.3. Reputable Design – Construction Unit
Installing a crane is a technical process requiring high precision. Choosing a reputable unit will know how to calculate, consult, and construct according to safety standards, minimizing risks during use. Many businesses encounter incidents just because they choose cheap contractors lacking inspection certificates or practical experience. Therefore, the reputation factor should not be the last choice but must be placed on top right from the beginning of the project.
6.4. Periodic Crane Maintenance
Cranes are equipment with continuous operation nature and often bear large loads, so periodic maintenance cannot be ignored. If not checked at the right time, small technical errors can accumulate and cause serious damage, even leading to occupational accidents.
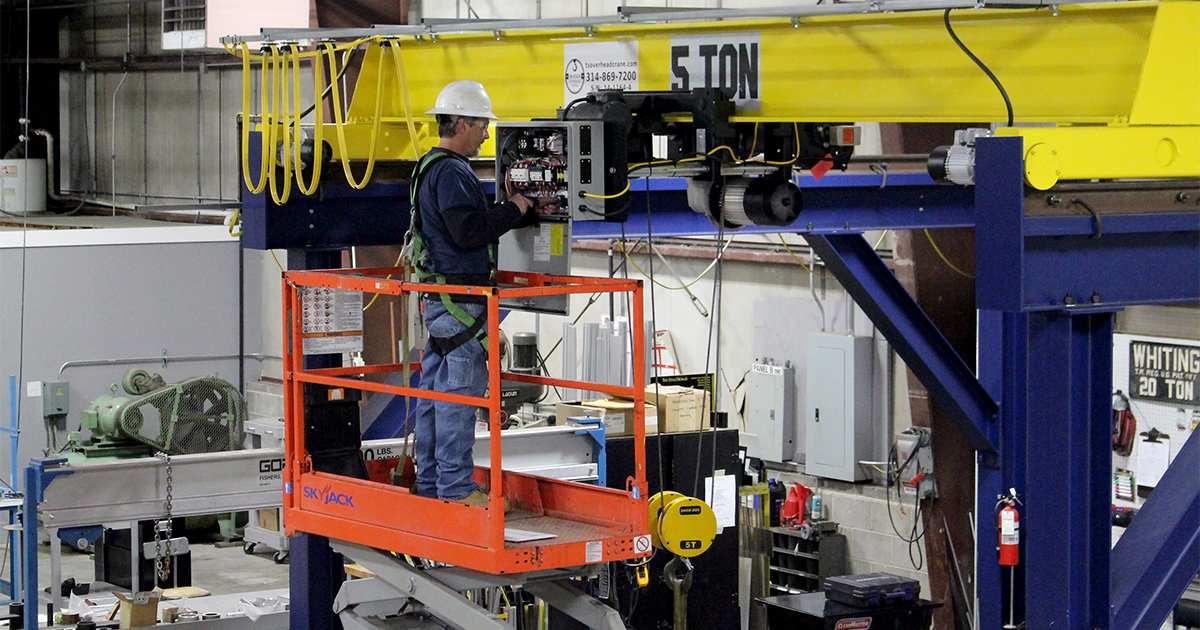

Periodic checking and maintenance of cranes.
When choosing a crane, businesses should prioritize product lines with easily accessible control systems, common components, and select suppliers with full after-sales service. A clear maintenance process will help the device maintain stable performance and significantly extend its life.
Conclusion
Modern factories cannot lack a professional and safe lifting system. When designed with the correct load, installed according to technical standards, and inspected periodically, the factory overhead crane will become an industrial lifting device playing the role of a link helping businesses shorten production time, save costs, and ensure long-term safety. Therefore, instead of viewing this as an initial investment, businesses should view the overhead crane as a long-term strategic factor that needs to be calculated methodically from the start.
Warehouse for lease in Vietnam | Warehouse for rent in Vietnam | Factory for lease in Vietnam | Factory for rent in Vietnam










