Understanding the Most Standard Industrial Factory Cooling System
January 22, 2026 07:26 AM
In industrial production, the cooling system plays an important role in maintaining stable working conditions, supporting efficient equipment operation, and ensuring worker safety. However, to achieve optimal efficiency, the system needs not only to simply cool but also to meet standards for performance, energy saving, and suitability for factory specifics. 1. What is a Cooling […]
In industrial production, the cooling system plays an important role in maintaining stable working conditions, supporting efficient equipment operation, and ensuring worker safety. However, to achieve optimal efficiency, the system needs not only to simply cool but also to meet standards for performance, energy saving, and suitability for factory specifics.
1. What is a Cooling System? Why Do Factories Need a Cooling System?
1.1. Concept of Cooling Systems in Industry
An industrial cooling system is a collection of equipment and technical solutions designed to maintain temperature and humidity in the factory at a stable level, suitable for production conditions. Depending on the scale, industry specifics, and working environment, the cooling system may include ventilation fans, evaporative cooling machines, central air conditioning systems (HVAC), or combined solutions.
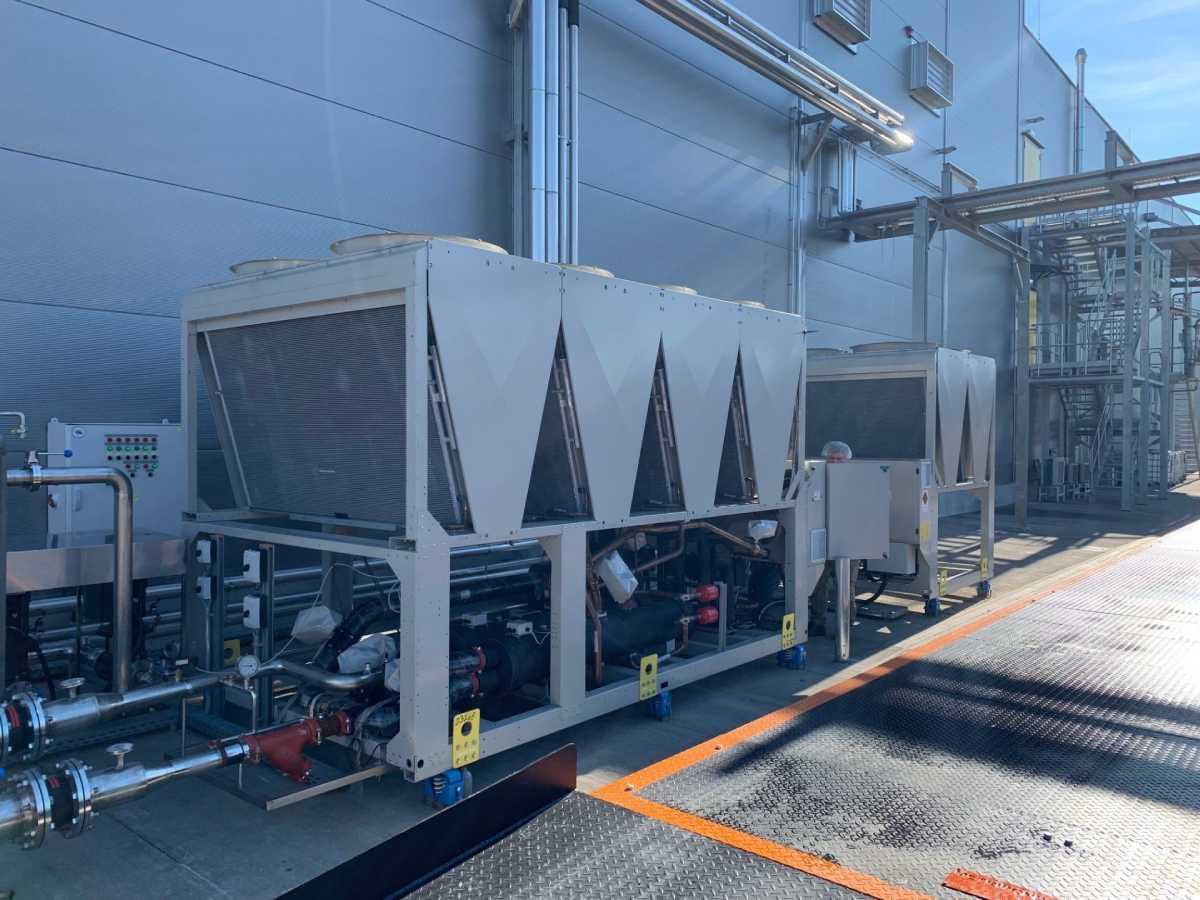

Cooling system.
1.2. Problems Without an Effective Cooling System
Decline in Health and Labor Productivity In the hot season, the temperature inside the factory can exceed 35–40°C. A stuffy environment causes workers to easily become dehydrated, tired, have difficulty breathing, and reduces concentration and reflexes. This condition will affect physical health, causing a significant decline in labor productivity, while increasing the risk of accidents during work.
Increased Risk of Equipment Damage High temperatures reduce the heat dissipation capability of equipment, especially industrial machines operating continuously. When operating in a hot environment for a long time, parts such as bearings, circuit boards, and lubricating oil will degrade quickly, leading to technical incidents such as motor burnout, short circuits, requiring machine stoppages for repair or replacement.
Unstable Product Quality In many industries such as electronics, food, printing, garments, etc., unstable temperature and humidity conditions can deform raw materials, cause adhesion errors, color fading, and change product structure. This leads to a high rate of defective goods, affecting reputation and business efficiency.
Disruption of Production Process In cases where both humans and machines cannot operate stably due to high temperatures, the production line is easily interrupted. Break times between shifts increase, machines must stop to cool down or for emergency maintenance – causing production progress to be delayed, reducing output and the ability to fulfill orders.
Increased Risk of Fire and Safety Loss Factories often store many flammable materials such as fabric, paper, plastic, chemicals, etc. Without a standard cooling system and ventilation, heat accumulation points will easily become ignition sources. Especially, industrial dust combined with dry air and static electricity can cause fires or serious electrical accidents.
1.3. Role in Equipment Protection and Enhancing Work Performance
As analyzed above, the lack of an effective cooling system can cause serious impacts on production activities and worker health. Conversely, when the working environment is well-controlled in terms of temperature and humidity, the factory will operate more stably, safely, and effectively. The cooling system brings many clear benefits:
- Protect machinery, extend equipment life: A cool environment helps machines dissipate heat effectively, limiting overheating phenomena that cause short circuits, motor burnouts, and component damage. It creates conditions for equipment to maintain stable performance and require less maintenance and repair.
- Maintain production line operational performance: Once the temperature in the workshop is properly controlled, machines run smoothly, without slowing down or stopping suddenly due to excessive heat load. The production line thus takes place continuously, ensuring progress and output.
- Improve worker efficiency: An airy, comfortable environment helps workers maintain higher physical strength, spirit, and concentration throughout the shift. As a result, labor productivity increases and the error rate is significantly minimized.
- Reduce risk of interruption and production loss: Thanks to the efficient cooling system, both people and equipment maintain a stable operating state. Well-controlled environmental temperature will minimize technical errors, defective products, and occupational accidents. Consequently, businesses minimize troubleshooting costs and maintain planned production schedules.
- Optimize long-term costs: Instead of spending on machine repairs, fixing defective goods, or overtime due to interrupted production, businesses can optimize operations, save costs, and improve long-term financial efficiency if they invest in a suitable cooling system.
2. Popular Types of Factory Cooling Systems Today
Depending on the area, production specifics, and investment level, each factory will be suitable for one or a combination of different cooling systems.
2.1. Industrial Fan Cooling System
This is the most basic and cost-saving solution, often using high-capacity fans such as standing fans, wall fans, exhaust fans, or axial fans.
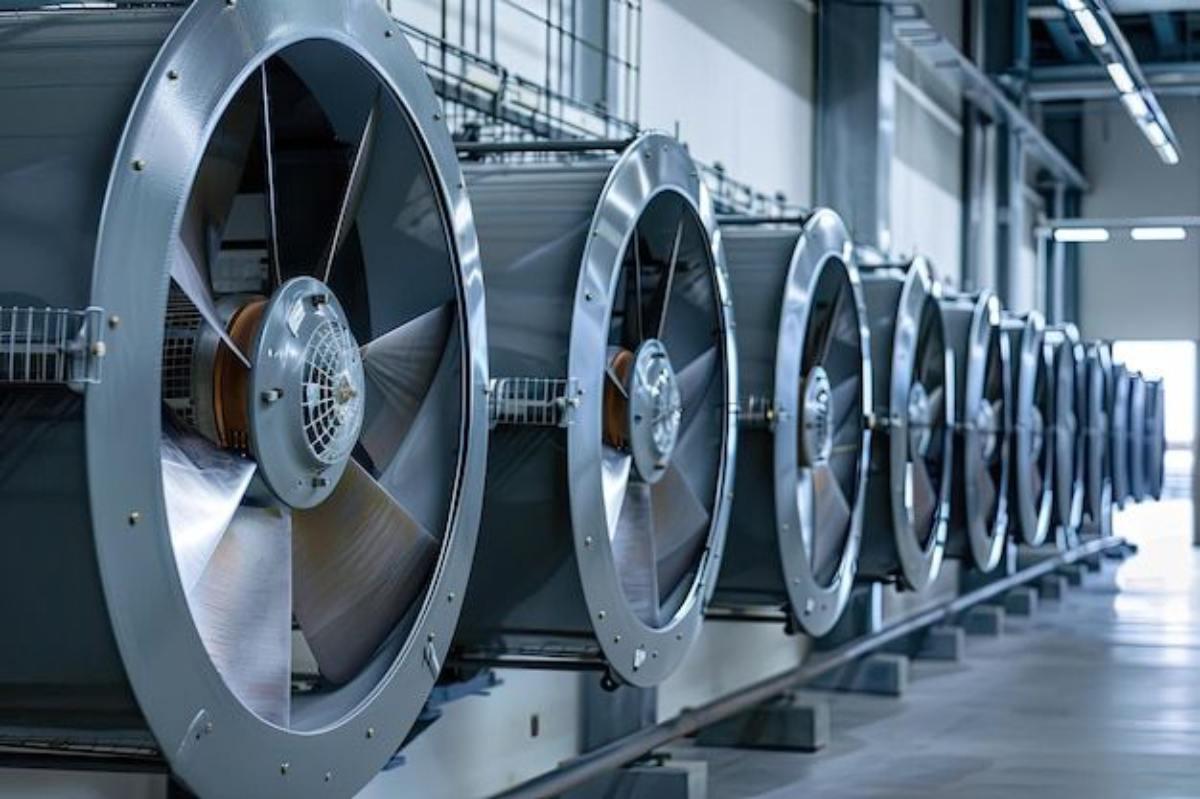

Fan cooling system.
- Pros: Cheap price, easy to install, low power consumption.
- Cons: Low cooling efficiency in closed environments and cannot control humidity.
- Suitable for: Small factories, not requiring strict temperature control.
2.2. Evaporative Cooling System (Cooling Pad)
This is a system using cooling pads combined with exhaust fans to draw hot air through a moist surface, thereby reducing the temperature before bringing it into the factory.
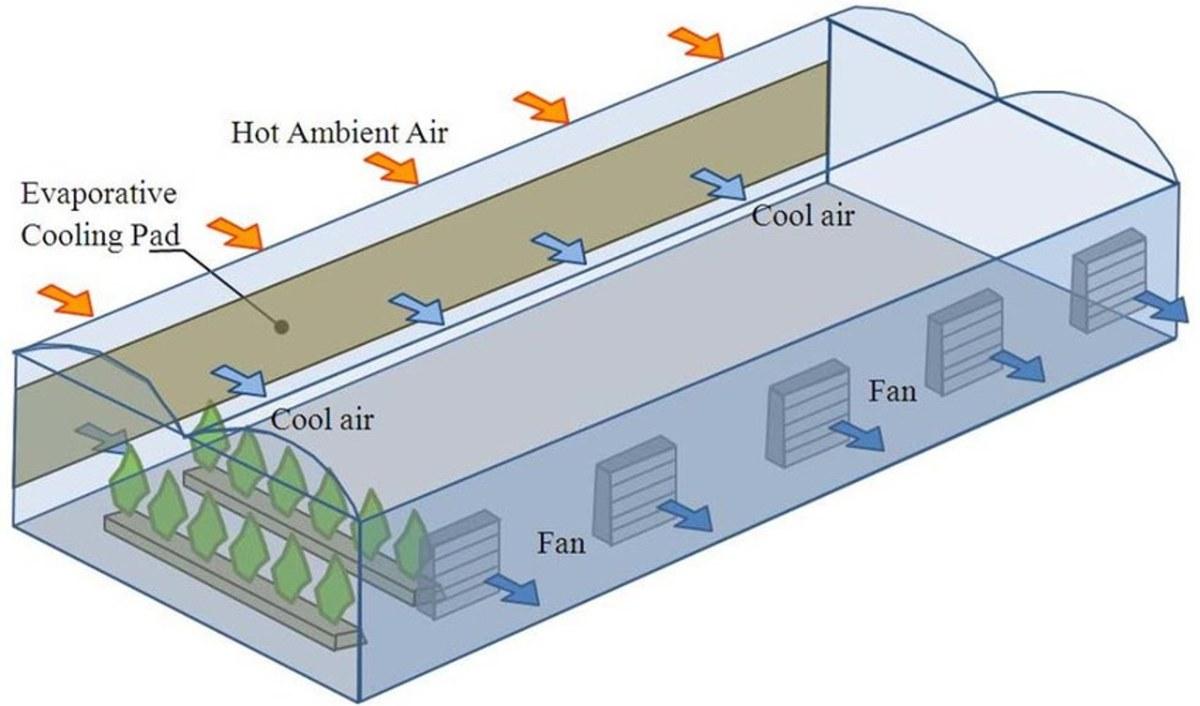
Technical illustration of evaporative cooling system.
- Pros: Fast heat reduction (5–10°C), more electricity-saving than air conditioning, maintains good air humidity.
- Cons: Needs periodic maintenance of cooling pads, efficiency depends on ambient humidity.
- Suitable for: Medium-scale factories with a need for wide-area cooling at moderate costs.
2.3. Central HVAC System
HVAC (Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning) is an integrated air conditioning system that controls temperature, humidity, and air quality.
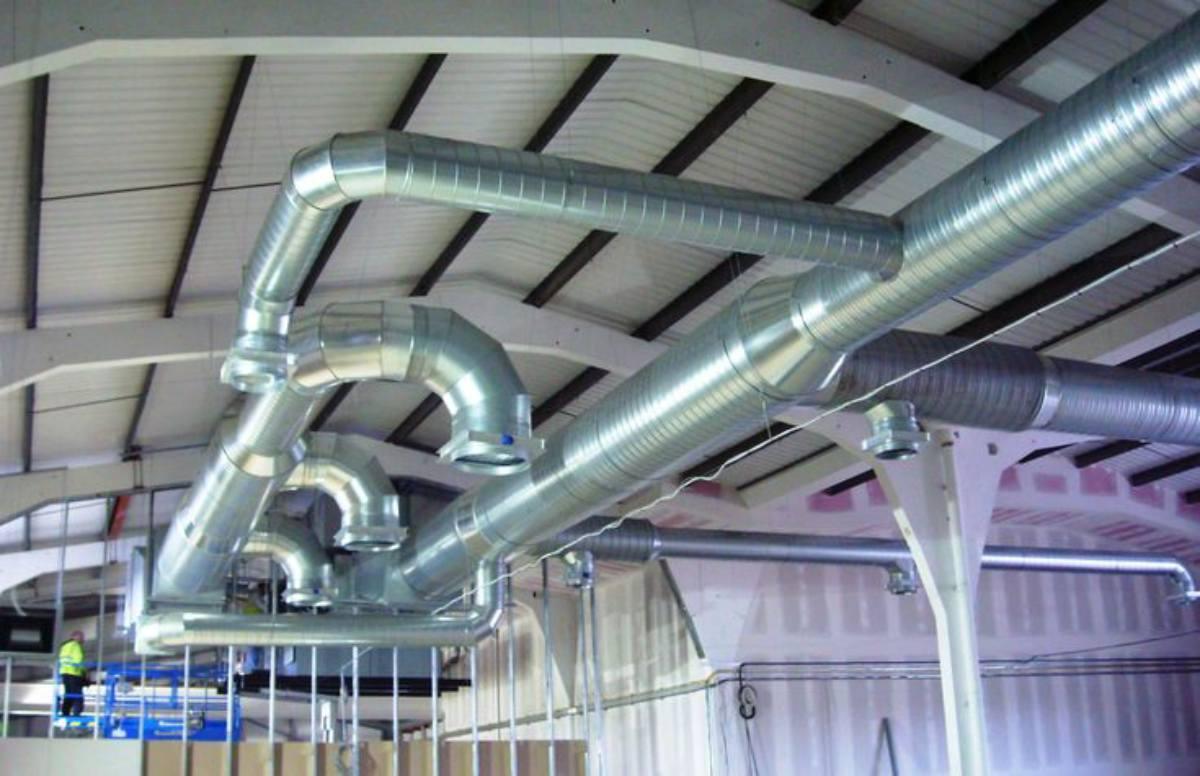

Central air conditioning system.
- Pros: Precise control of temperature and humidity, suitable for strict production environments.
- Cons: High investment and operating costs, requires specialized installation and maintenance techniques.
- Suitable for: Food, pharmaceutical, and electronic manufacturing factories – places needing a closed and absolutely stable environment.
2.4. Misting Cooling System
This system uses high water pressure to create fine mist particles through nozzles, helping to cool the air quickly through the natural evaporation process.
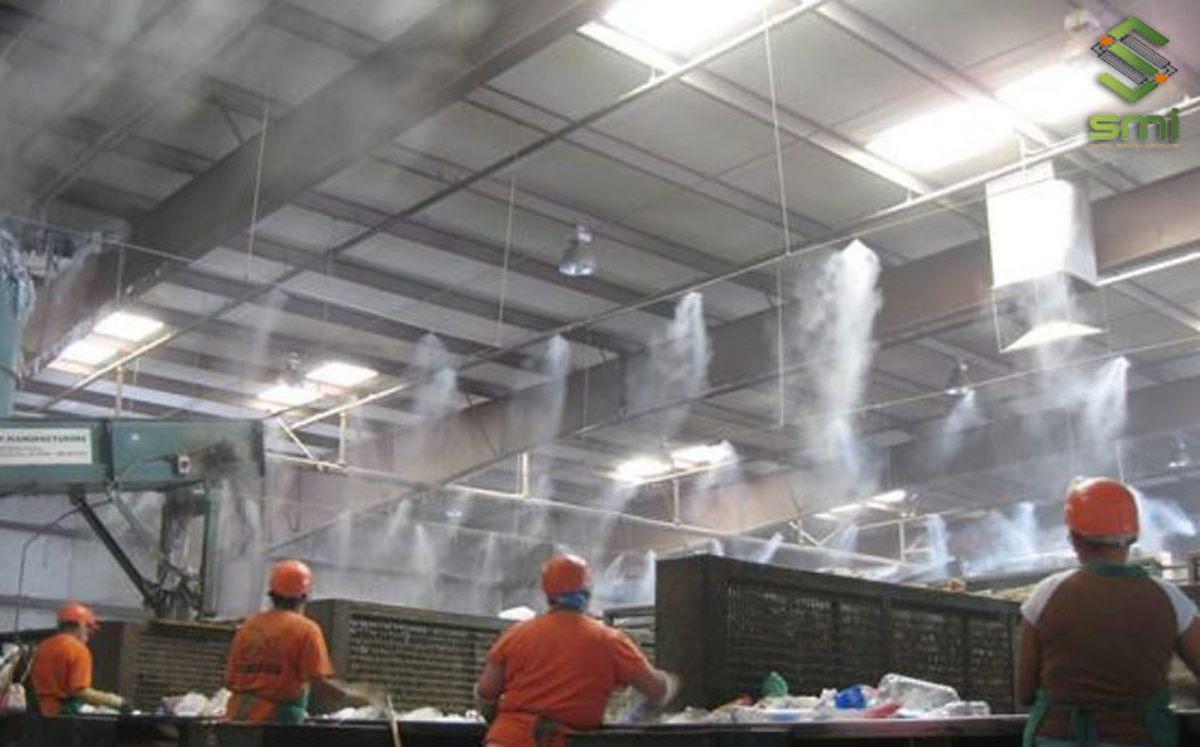

Misting cooling system.
- Pros: Low cost, fast cooling, easy construction.
- Cons: Causes wet floors and equipment if used incorrectly, can affect the production line.
- Suitable for: Outdoor areas, production workshops not too sensitive to humidity.
2.5. Natural Ventilation Combined with Cooling
This system utilizes the pressure and temperature difference between inside and outside to create natural air circulation, combined with supporting devices such as exhaust fans, louvers, or skylights to enhance cooling efficiency and ventilation for the factory.
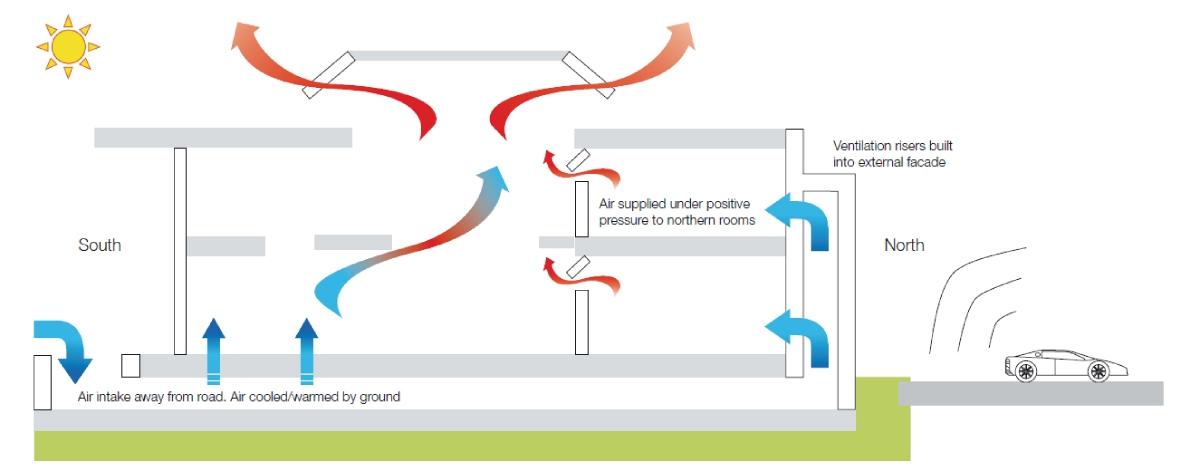
Operating principle of natural ventilation system.
- Pros: Saves electricity, environmentally friendly, low maintenance cost.
- Cons: Heavily dependent on weather conditions, not highly effective on extremely hot days.
- Suitable for: Newly built factories, prioritizing energy-saving and environmentally friendly solutions.
3. Evaluation Standards for an Effective Factory Cooling System
To bring real efficiency, any cooling system needs to meet specific technical criteria. A cooling system is considered effective when ensuring the following factors simultaneously:
3.1. Temperature and Humidity Reaching Standard Thresholds
The most important factor is the ability to control temperature and humidity in the factory. According to the world’s leading association in the field of air conditioning and ventilation (ASHRAE), a standard factory cooling system needs to maintain the working environment temperature below 32°C and humidity fluctuating between 55–70% to ensure safety for workers and equipment.
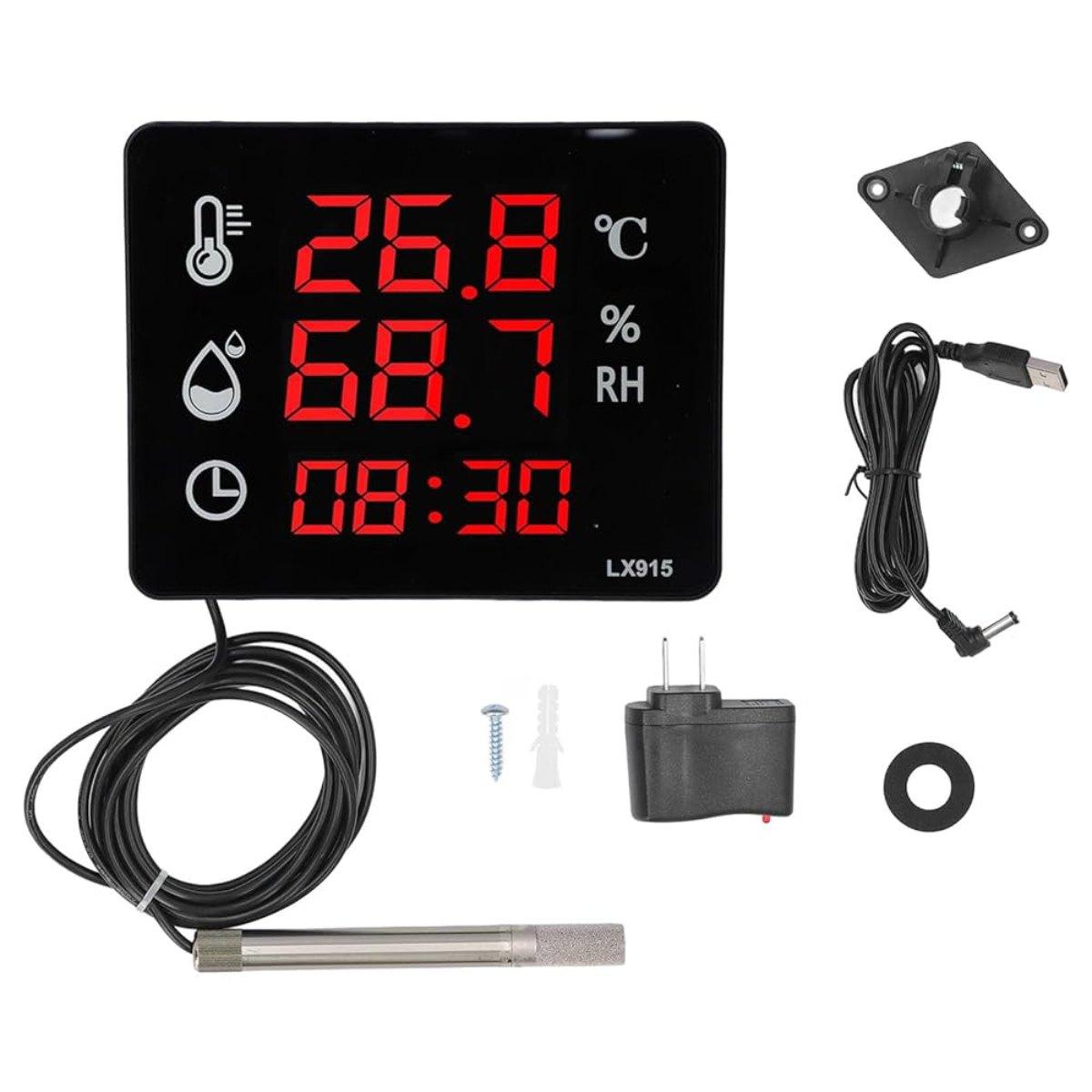

Temperature and humidity reaching standard thresholds.
3.2. Energy Saving Capability
A cooling system is evaluated as energy-saving when it operates efficiently without consuming too much electricity compared to actual needs. A standard system needs to:
- Minimize power waste during off-peak hours or in less-used areas.
- Be capable of flexible operation, adjusting capacity according to actual conditions (thanks to controllers, sensors, or power-saving technology).
- Maintain stable cooling performance without causing sudden spikes in electricity costs.
3.3. Coverage and Air Circulation
An effective cooling system needs to ensure airflow is distributed evenly throughout the factory space. Good air circulation supports maintaining stable temperatures, limiting local hot spots, and creating a comfortable working environment for workers. According to ASHRAE industrial ventilation design standards, the average wind speed in the factory should reach 0.5–1.5 m/s, depending on the type of production and the activity level of workers, to ensure comfortable and safe working conditions.
3.4. Durability and Long-term Operating Costs
The cooling system needs to ensure stable operation capability for many years without incurring excessive maintenance costs. Equipment such as industrial fans, cooling pads, or nozzles need to have high durability, low failure rates, and be easy to replace.
4. How to Choose a Cooling System Suitable for Your Factory
There is no single solution for every factory. Choosing a cooling system needs to be based on many practical factors to ensure efficiency, savings, and suitability for operational needs.
4.1. Based on Factory Area and Structure
Area and ceiling height determine the amount of air needed to cool, while also affecting wind distribution efficiency.
- For small factories with low ceilings, industrial fans or simple misting systems can be used.
- For wide spaces, high ceilings, or areas divided into many zones, it is necessary to combine intake-exhaust systems or cooling pads to ensure even air circulation.
4.2. Based on Production Characteristics (Heat Generation)
The nature of production activities in each industry will create different heat levels, directly affecting the cooling requirements of the factory.
- For industries with high heat levels such as metallurgy, heavy mechanics, food processing, etc., priority should be given to systems with deep cooling capability and large air flow to ensure a stable working environment.
- Conversely, industries generating less heat such as garments, electronic component assembly, etc., can use more economical solutions such as industrial fans, misting, or natural ventilation while still ensuring efficiency.
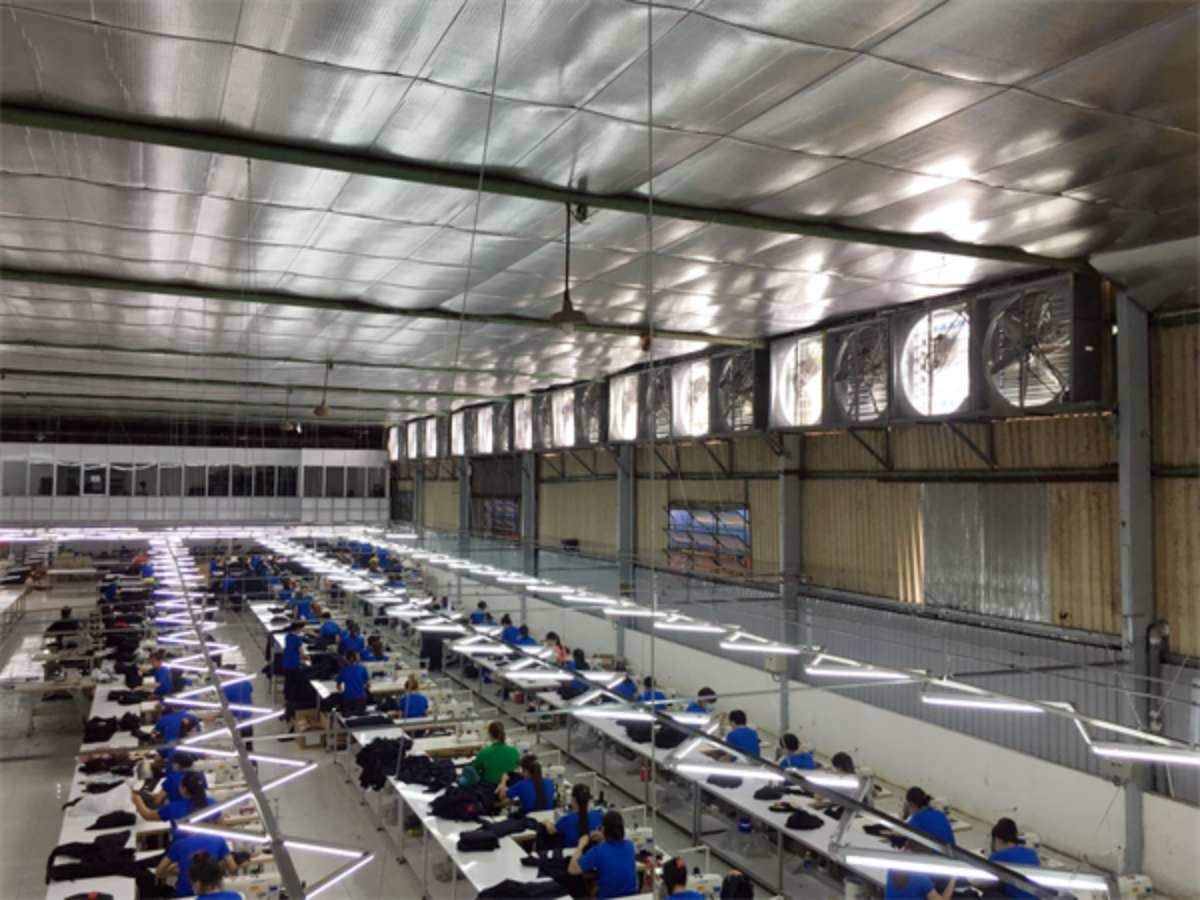

Ventilation fan cooling system in garment factory.
4.3. Analyzing Initial Investment and Operating Costs
The financial efficiency of a cooling system needs to be evaluated based on both investment costs and long-term usage costs. Fully analyzing cost items helps businesses avoid choosing solutions that seem economical but are costly later. Consider the balance between initial procurement costs (equipment, materials, installation) and periodic operating costs (electricity, maintenance, component replacement). Prioritize solutions with a reasonable Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), ensuring real savings throughout the usage lifecycle. For factories operating continuously, priority should be given to systems with high reliability and stable operating costs over time, rather than just considering the initial purchase price.
5. Suggested Effective Cooling Models for Factories Today
Each cooling system has a different operating principle and application range. Understanding how it operates as well as the strengths and limitations of each model will help businesses make optimal choices, suitable for production specifics as well as practical deployment conditions.
5.1. Combining Industrial Fans and Cooling Pads
This is one of the cooling models widely used in many factories thanks to stable efficiency and reasonable investment costs. This cooling system operates on the principle that industrial fans create large air flow to suck hot air out, while cooling pads help lower air temperature thanks to the water evaporation process. After the cooling process, the air will be cool, slightly humid, and distributed evenly in the production space. This model is suitable for medium to large-scale factories with continuous production characteristics and not requiring overly strict temperature control, typically such as garments, wood processing, food, or packaging.
5.2. Applying HVAC Systems in High-Standard Factories
HVAC (Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning) is a central air conditioning system capable of comprehensively controlling environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and air quality.
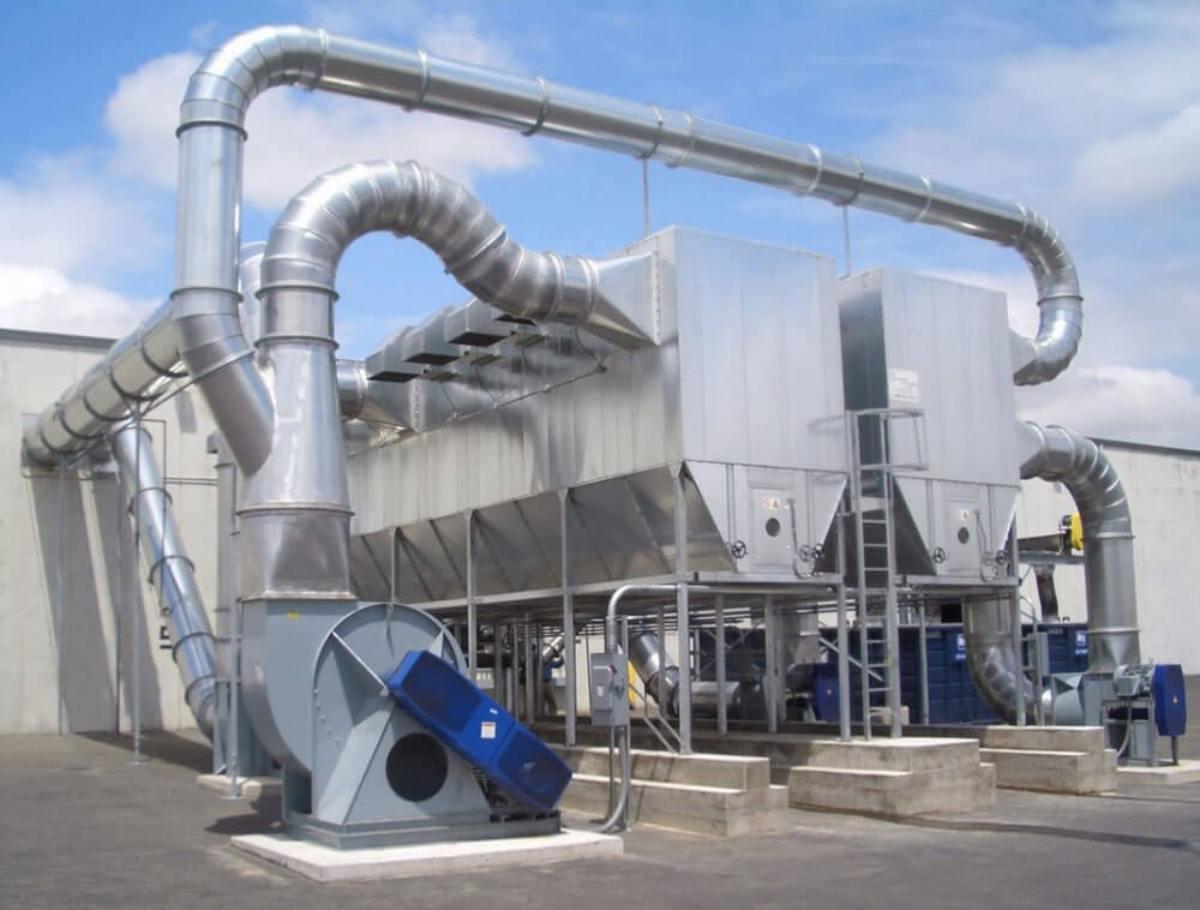

HVAC system in high-standard factory.
This system typically uses a network of ducts and central processing equipment to ensure air is filtered clean, cooled stably, and distributed evenly throughout the factory. With the ability to meet high standards for working environments, HVAC is an almost mandatory choice for industries requiring high precision in production conditions, such as electronic component manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, high-end packaged food, or cleanrooms. However, the initial investment and operating costs of this system are quite high, more suitable for businesses with large budgets and strict technical requirements.
5.3. Hybrid Solution: Cooling + Ventilation + Energy Saving
With the trend of energy optimization and operational flexibility, many businesses today choose the hybrid model – integrating multiple cooling methods such as exhaust fans, misting, natural ventilation, and temperature control sensors. The biggest advantage of this model is the ability to adjust according to time and actual conditions, helping to save electricity and reduce operational pressure in the hot season. This solution is often deployed in medium and large factories with many different functional areas, or places with a need to renovate old systems without too high investment. Hybrid is an ideal choice for businesses aiming for sustainable development, wishing to balance cooling efficiency and operating costs.
Conclusion
Correctly understanding the cooling system and choosing the appropriate solution is the first step to building an efficient, stable, and safe operating factory. No model is perfect for everyone, but a standard system always needs to meet practical needs well, save energy, and be suitable for long-term operating conditions.
Warehouse for lease in Vietnam | Warehouse for rent in Vietnam | Factory for lease in Vietnam | Factory for rent in Vietnam










